Functional testing focuses on checking the software functions against the defined requirements. The aim of this quality assurance process is to ensure that each function works correctly and meets user requirements. Each component of the software is tested to ensure that the final product works properly.
“Functional testing usually describes what the system does.”1
In today's fast-paced software development environment, functional testing is essential to ensure that your applications are reliable, user-friendly and bug-free.
QF-Test supports the record-replay paradigm going way beyond it. This allows any person to create simple to very complex tests for the software. Software programming skills are not necessarily required although we know they help. Get advice now.
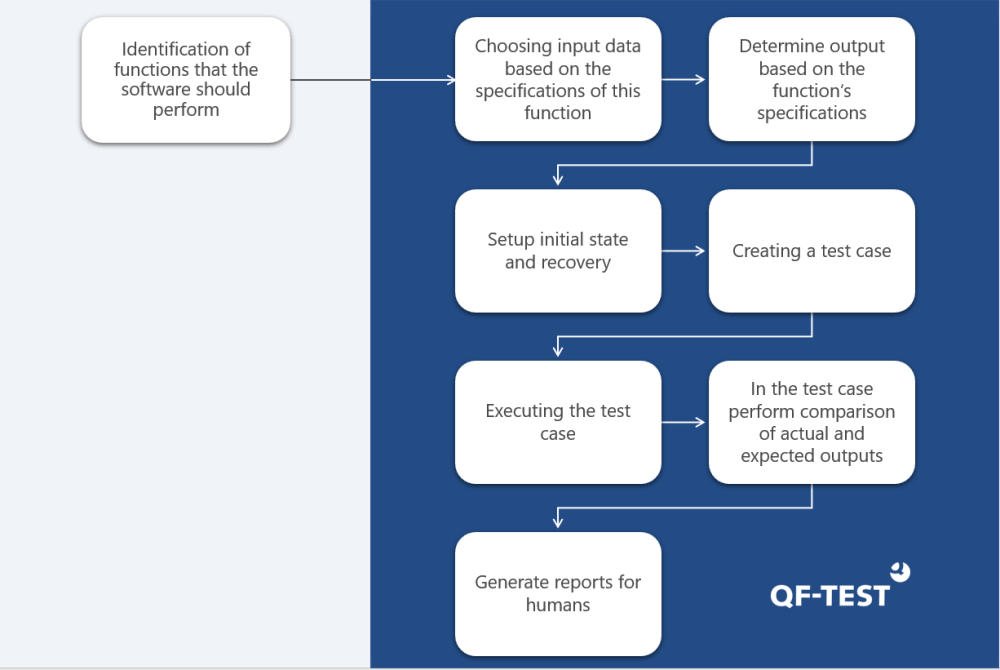
In step 1 those functions are traditionally described in external to QF-Test files. One can also use a Keyword-Driven-Development (KDD) or Behavior-Driven Testing (BDD). Both are very well supported by QF-Test. A special parser library for Gherkin (a language of Cucumber) is also available on demand.
The values required for steps 2 and 3 can be described via the usage of Data-Driver. The data can be fed via database, internal tables, external CSV or Excel files and more. This type of testing is often called Data-Driven testing, especially useful when multiple values need to be tested in similar tests and conditions.
Step 4 has a very special place within QF-Test. The QF-Test dependencies, a unique feature that takes care of setup, cleanup, error handling and recovery of the system under test (SUT).
Steps 5, 6 and 7 belong to the execution and reporting engine of QF-Test. Reporting, screenshots, re-run, and test documentation are only part of the features. Integration with all Continuous Integration tools, like Jenkins is also possible.
Normally step 8 wouldn't need an explication, since you and your colleagues want to work with the test results and your manager wants to be informed about them.
Read how our customers have benefited from our customized testing solutions. Our case studies show you concrete examples of how we have improved the quality and reliability of software projects in different industries and of different sizes.
Ready to take your software quality to the next level? Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive functional testing solutions. Together, we'll make sure your software meets the highest quality standards and delights your users.
report their
QF-Test experiences
report their
QF-Test experiences
report their
QF-Test experiences
1. Functional cookies
We use functional cookies to ensure the basic functionality of the website.
2. Performance and statistic cookies
We use Matomo for analyzing and optimizing our website. Cookies permit an anonymous collection of information that help us offering you a clear and user-friendly visit of our web pages.
This cookie contains a unique, pseudonymized visitor ID internal to Matomo for recognizing returning visitors.
This cookie is used to track from which website the anonymized user proceeded to our website.
The Matomo session cookie is used to track the visitor's page requests during the session.
is created and should be then directly deleted (used to check whether the visitor’s browser supports cookies).
short lived cookies used to temporarily store data for the visit.
short lived cookies used to temporarily store data for the visit.